Table of Contents
Diabetes is a chronic health condition, which affects almost every organ of the body. Good diabetic control depends on proper management. Management of the disease requires regular blood glucose monitoring.
Diabetic patients must endure the uncomfortable and often painful process of pricking their finger every time they use a glucometer to monitor their blood glucose levels, which is typically necessary three times a day.
An effective strategy that minimizes or eliminates pain should be implemented; various devices have been developed, and some are now available to the public, such as needleless diabetes sensors that can be placed on the skin.
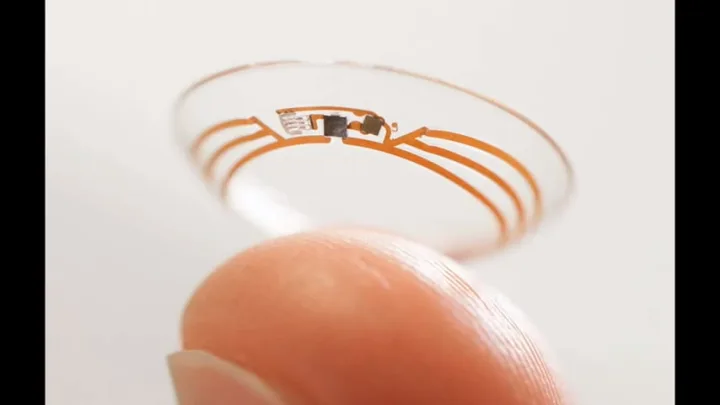
Likewise, a team of researchers at the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) has developed a biosensing contact lens capable of detecting glucose levels in patients with diabetes. They published their findings in Science Advances.
Controlling sugar levels for diabetic patients is of great significance. High blood glucose levels can be hazardous for diabetic patients. An enzyme-based finger pricking method is the most frequently used technique in a diabetic evaluation. This is the method through which compliance can be reduced in diabetic patients.
Many struggles are made to monitor the glucose level in tears with a smart contact lens.
How Does Diabetic Contact Lens Work?
This contact lens use electrode that comprises highly malleable and clear material. This transparent and flexible lens also suppresses a glucose sensor that sends electrical signals to LED.

With this sensor’s help, patients can convey their health information in real-time using the embedded wireless antenna in the lens.
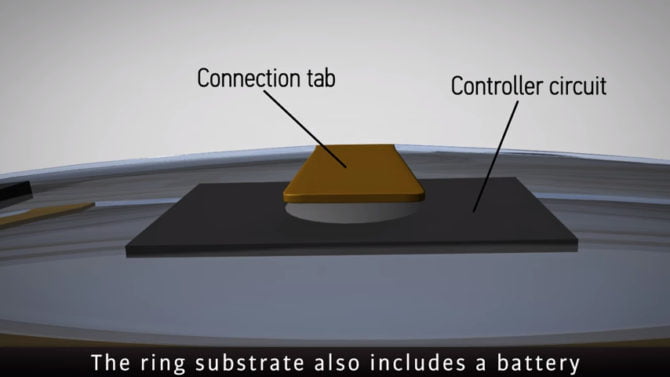
The electric power that operates the LED pixel and the glucose sensor is transmitted to the lens through the antenna. Therefore, the LED pixel will turn off when the tear fluid’s glucose accumulation exceeds the threshold.
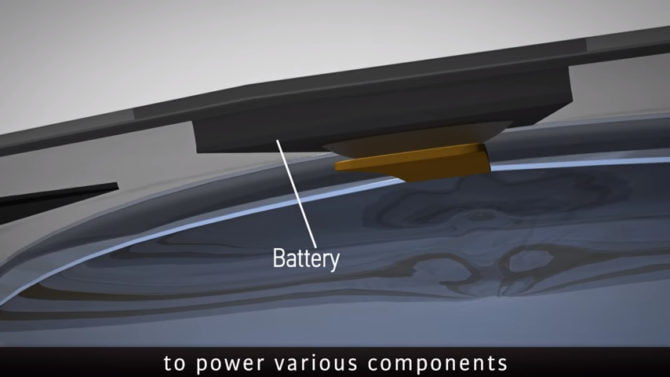
The research team experimented on a live rabbit. The rabbit showed no abnormal behavior during the eye blinks, and the LED pixel was turned off.

When the glucose concentration in tear fluid is noted, and above the threshold, the intelligent contact lens can maintain the eye temperature accurately.
Some issues with these contact lenses
Some experts from Google and Novartis believe that tears have not proven to be reliable in measuring glucose. For example, former CSO of J&J’s Scan John Smith said that measuring glucose from the blood, saliva, and tears has failed for decades.
These readings get impacted by temperature, surrounding environment, and humidity.
Conclusion
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic health condition marked by increasing blood glucose levels. It requires regular monitoring for reasonable control. According to these measurements, one can know the need for further therapy if needed or for checking whether the current therapy is working optimally or not. Patients have been using multiple needle pricks for this purpose. This has been painful for the patients. Thus, for diabetics, needless diabetic care and contact lenses for sensing blood glucose levels are also included among many underway things.
There are concerns, however, about the use of these contact lenses. They may not predict the accurate glucose level, as some researchers suggested. More investigations need to be done. But, if can make a massive difference if it’s proven for use in the future.




Share Your Thoughts