Ultraviolet light is a type of electromagnetic radiation.
Ultraviolet light, including both UVA and UVB, is the main cause of both summer tans and sunburns. The effects of UV radiation on the human body can be quite detrimental, and it is important to take precautions to protect the skin. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays can lead to premature aging, wrinkling, and even an increased risk of developing skin cancer. It is therefore crucial to always be mindful of sun protection methods such as wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen, seeking shade when the sun is at its strongest, and wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses. Keeping in mind that UV radiation can be damaging to the living tissue, it is essential to strike a balance between enjoying the sunshine and preserving our health.
Ultraviolet light is not detectable by the human eye. But some insects are able to see ultraviolet light. Our bodies use ultraviolet light to make vitamin D. If the ultraviolet light exposure is too much, then it can be very harmful as it can cause cancer.
When Ultraviolet light descends on certain materials, ultraviolet light may cause them to fluoresce. It emits electromagnetic radiations of lower energy, such as visible light. Ultraviolet light, when it interacts with specific substances, has the ability to induce fluorescence. This phenomenon occurs due to the emission of electromagnetic radiations of lesser energy, such as visible light.
Table of Contents
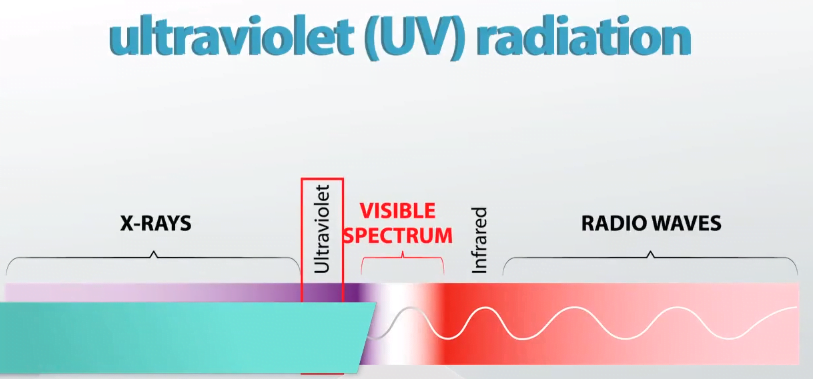
The range of ultraviolet light:
Ultraviolet radiation lies between wavelengths of about 400 nanometers (1 nanometer [nm] is 10−9metre) on the visible-light side and about 10 nm on the X-ray side, though some authorities extend the short-wavelength limit to 4 nm.
Regions in which ultraviolet light is divided:
Ultraviolet radiation is commonly divided into four regions:
- near (400–300 nm)
- middle (300–200 nm)
- far (200–100 nm)
- extreme (below 100 nm)
Divisions of ultraviolet light:
Based on the interaction of wavelengths of ultraviolet radiation with biological materials, three divisions have been designated:
1. UVA (Ultraviolet A): This is the longest wavelength among the three divisions, with a 320 to 400 nanometers range. UVA radiation penetrates the deepest into the skin and is mainly responsible for aging and wrinkling. It is also the type of UV radiation used in tanning beds.
2. UVB (Ultraviolet B): With a range of 280 to 320 nanometers, UVB radiation affects the skin’s surface layers. It is the primary cause of sunburns and is a major contributor to the development of skin cancer. UVB rays are strongest during midday when the sun is at its highest point in the sky.
3. UVC (Ultraviolet C): This is the shortest wavelength of the three divisions, ranging from 100 to 280 nanometers. Fortunately, UVC radiation is mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and doesn’t reach the surface. It is highly germicidal and is commonly used for disinfection purposes.
Understanding the different divisions of ultraviolet radiation is crucial for protecting ourselves from its harmful effects. By taking precautions such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure, we can minimize the risks associated with UV radiation.
How ultraviolet light is produced?
High-temperature surfaces, such as the Sun produce ultraviolet radiation.
It is produced in a continuous spectrum and by atomic excitation in a gaseous discharge tube as a discrete spectrum of wavelengths.
Most of the ultraviolet radiation in sunlight is absorbed by oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere, forming the lower stratosphere’s ozone layer. This layer of ozone acts as a shield, protecting life on Earth from the harmful effects of excessive UV radiation. It is important to note that the ozone layer absorbs the majority of the sun’s UVB radiation, which is known to be more damaging to living organisms. However, of the ultraviolet that does manage to reach Earth’s surface, almost 99 percent is UVA radiation. UVA rays are less energetic than UVB rays, but they still have the potential to cause skin damage and contribute to the aging process.
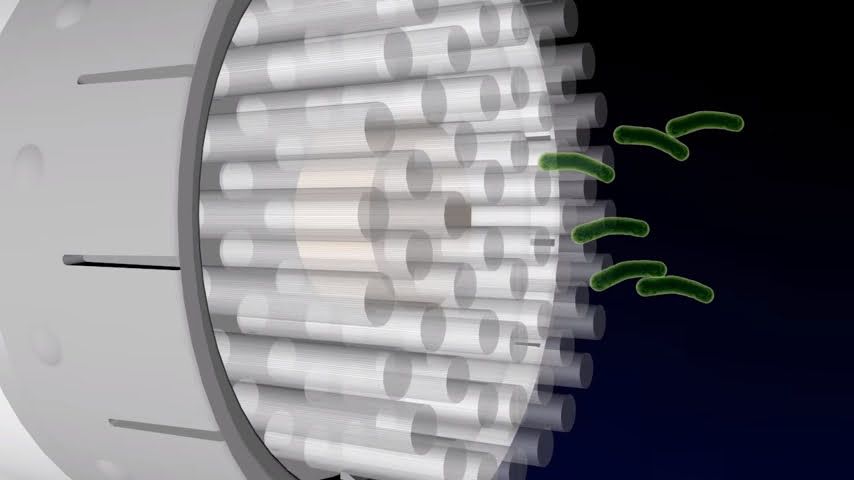
An ultraviolet UV lamp
An ultraviolet UV lamp has been developed that basically kills the influenza virus. A study has shown that it is not injurious to human eyes, skin, and health.

Objective:
This sophisticated technology has been developed with the primary objective of intercepting the transmission of seasonal flu in various public settings, including but not limited to schools, hospitals, restaurants, libraries, offices, parks, stores, and many more. It is worth noting that ultraviolet light, renowned for its exceptional effectiveness and efficiency, plays a pivotal role in eradicating germs, microbes, bacteria, and viruses, thereby contributing significantly to public health and safety.
UV devices:
There are UV devices that have been widely utilized for the purpose of sterilization and ensuring the cleanliness of medical equipment within hospital premises. With their ability to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms, these UV devices play a vital role in maintaining a hygienic environment in healthcare settings. By utilizing ultraviolet technology, these devices have proven to be invaluable tools in safeguarding the health and well-being of both patients and medical professionals.
But the conventional germicidal lamp is not safe for humans when they are around.
Can Coronavirus be killed with UV Light?
There’s only one type of UV that can reliably inactivate Covid-19 – and it’s extremely dangerous.
BBC.com
According to BBC.com and some researchers, it’s not a good idea or even impossible. Learn more here.
UV light can effectively kill airborne influenza:
UV light has been proven to be highly effective in eliminating airborne influenza. This powerful tool can successfully eradicate bacteria while still ensuring the safety of human tissues. A study conducted by experts, as mentioned in the linked article (source), provides evidence that broad-spectrum germicidal UV light, with wavelengths ranging from 200 to 400 nanometers, is remarkably successful in eradicating bacteria, microbes, and viruses. This process occurs by disrupting the molecular bonds responsible for holding the DNA together. With these impressive findings, it is clear that UV light is a valuable tool in the fight against the spread of influenza.
This conventional UV light is used to sterilize medical equipment. The conventional germicidal UV is also harmful to human health. It can cause skin cancer.
Brenner and his colleagues hypothesized that a narrow spectrum of ultraviolet light called far-UVC could destroy microbes without damaging healthy tissue.
UVC light has a very limited range, and it cannot go through the outer dead cell layer of human skin or the tear layer in the eye. However, it is not harmful to human health.
Conclusion:
Ultra-violet rays can provide numerous benefits of sterilization, i.e., removing microbes and viruses from the equipment. Additionally, they have the capability to effectively reduce the transmission of illnesses caused by these harmful pathogens. Notably, there is a special emphasis on the transmission of the influenza virus; however, the practical application of ultraviolet rays extends beyond eradicating these viruses. The utilization of UV rays is instrumental in rendering equipment free from microorganisms and viruses, thereby significantly minimizing the risk of infectious diseases.
Affiliate Disclaimer: TechEngage participates in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases through links to Amazon.com and its affiliated sites. For more information, please read our disclaimer.